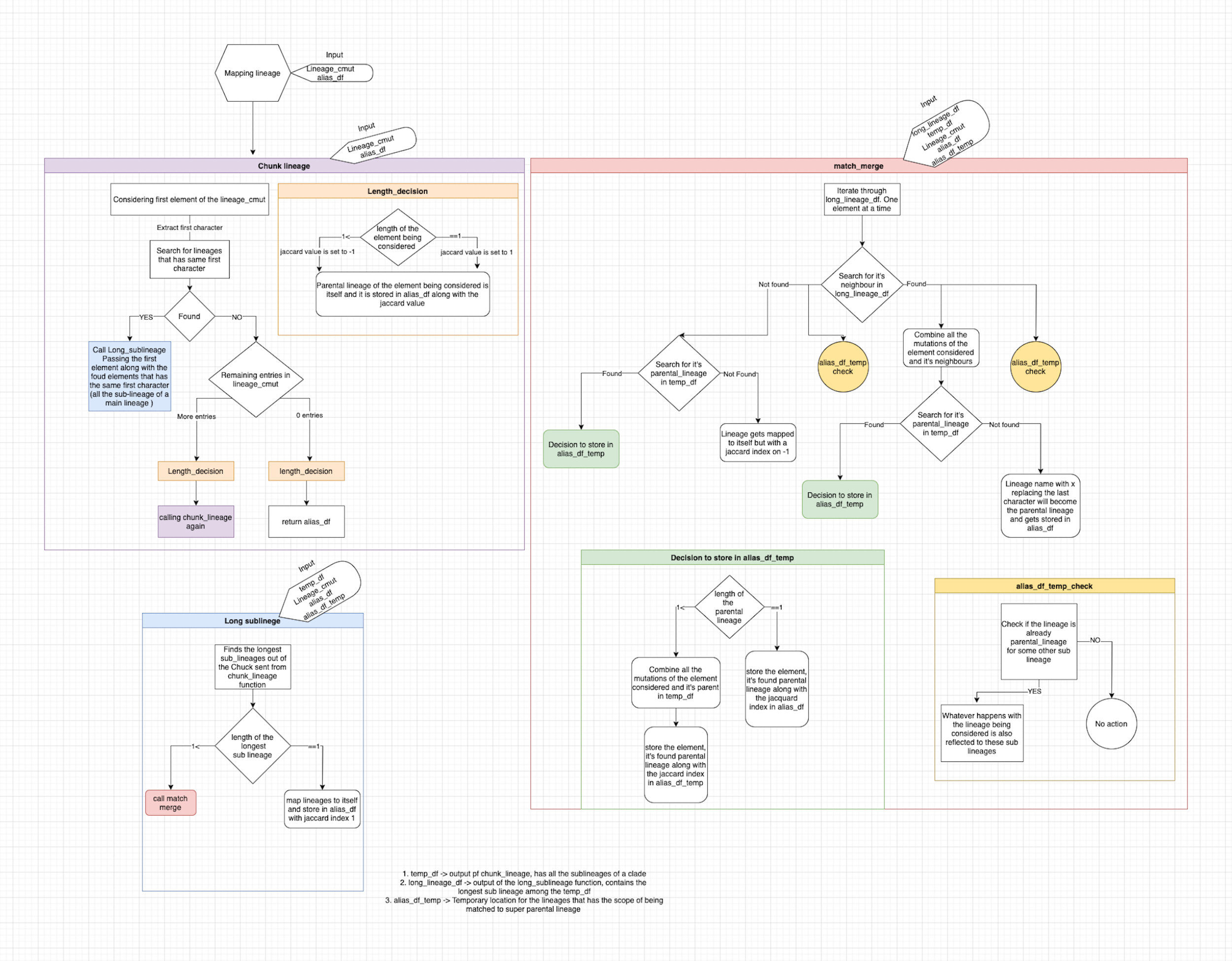
Mapping_lineages
Function mapping_lineages (lineage_cmut,alias_df)
Function chunk_lineage(lineage_cmut,alias_df)
1.Chunks lineages and sublineages by the first character of Pangolin string.
One element of the input data frame is considered at an instance and all the
members of the clade to which it belongs are chunked and passed to the downstream
processing.
2. If there are no lineages having the same first
character but there are entries in the input df, the lineage is
mapped to it's own and is stored in alias_df.
3. else If the there are no more entries in the
lineage_cmut then the lineage is mapped to itself and return is called.
4. else the chunk stored in temp_df is passed to
long_sublineage
End
Function long_sublineage(temp_df,lineage_cmut,
alias_df,alias_df_temp)
1. Finds the sublineage with longest character string
and stores it in longlineage_df
2. If multiple lineages have long character string
both the lineages are stored in longlineage_df
3. If linegaes length is just one then it is the
parental lineage and it is mapped to it's own and is
removed from temp_df amd is stored in alias_df
END
Function match_merge(longlineage_df,temp_df
lineage_cmut,alias_df,alias_df_temp)
1. Iterates through the longlineage_df, forms pattern
from the first element taken and tries to find
neighbours in longlineage_df based on jaccard value
using function find_jaccard
1. If neighbours are found their mutations are
combined (union).
2. Checks if these neighbors are paretnal lineage to
some other lineage in the alias_temp_df
3. Checking if there is a parental lineage to the
neighbours in the temp_df
4. If parental lineage is found and if the length of the parental
lineage string is more than one, the mutations of the
neighbours and the parernal lineages are again
combined (union) and stored in the place of
mutations of the parental lineage in temp_df. Neighbours are
mapped to their found parent and are stored in alias_df_temp,
since there is potential for surther mapping. This parental
lineage also becomes the parental lineage for the
sublineages that had these neighbours as parental
lineage in alias_df_temp.These neighbors are removed from
longlineage_df and the loop is iterated for the next round.
5. Else if the length of the parental lineage is
equal to 1 then everything in the previous point
that was written in the alias_df_temp is written to
alias_df. Mutations are not meddled with, since it is
the ultimate paretnal lineage and there is no go further.
6. If no parental lineage was found then the the
Neighbours are mapped to the pattern which is the
name of the neigbors without the last character. This
pattern concatinated with x becomes the parental
lineage of the neighbors. This also becomes the
parental lineage for those sublineages for which the
nighbors were parental lineage.
2. If there are no neighbors found
1. Code directly starts finding the parental
lineage for the element being considered.
2. If paretnal lineage is found and the length of
the lineage is more than 1, the element in hand
is mapped to the found paretnal lineage and jaccard
value is stored in the alias_df_temp. Mutations of
the element and the found parental lineage is combined and
stored in the place of the parental mutations in temp_df
3. Sublineages for which the lineage in hand is the parental
lineage in alias_df_temp gets mapped to the newly found parental lineage.
4. If the length of the parental lineage being
found is equal to one then point 2,3 is repeated
but difference would be that instaed of
alias_temp_df, alias_df is used and mutations are not meddeled with.
3. If no parerntal and neighbors were found
1. The lineage being considered is mapped to
itself.
2. For sublineages in the alias_df_temp that has
the lineage being considered as parental lineage is
remains the same. It is just transfered to
alias_df with no changes.
Once the longlineage_df has been fully processed if
there are entries in temp_df long_sublineage is called else chunk lineage is called.
END
End
Function find_jaccard(pat,search_df,pat_mutations=0)
search_lineage_loc<-grep(pat,search_df$lineage)
1. If pat_mutations==0 means the function is finding the
neighbours. Else the function is overloaded
to find the parental lineage.
2. If pat_mutations==0 the length(search_lineage_loc) should be
more than 1 - neighbours other than the lineage in hand.
3. If no neighbours were found then function returns
neighbours="0", jaccard_value=-1,neighbour_loc=0
4. Other than point 2 the overloaded function does the
same functionality for both the overloaded purposes
and returns jaccard value, neighbours, neighbour_loc
End
Function Find_parental(pat,parental_df)
1. Recursively searches with the pattern
until it finds the parental lineage satisfying
the conditions
2. The pattern is shortened every iteration.
End
 question on the treshold
question on the treshold
